If you type a question into a search engine like Google or Bing, you probably click on one of the top links.
After reading the article, you might eventually buy one of the products they recommend.
The companies that show up at the top of Google’s organic results (as pictured above) don’t have to pay a cent for clicks, which means they essentially get free customers to their website.
So, how can you get your website to appear at the top of Google?
While there isn’t a magic formula to rank on Google, search engine optimization (SEO) is a marketing strategy companies use to improve their chances of ranking at the top of Google for critical keywords.
In this article, we’ll discuss what SEO is, how it differs from other marketing channels, and the basics of implementing an SEO strategy.
Want us to
scale your traffic?
For the first time, The Copyblogger methodology is now available to a select few clients. We know it works. We’ve been doing it since 2006.
What is SEO in marketing?
In marketing, SEO is a process that helps websites improve their rankings and visibility in search engines. Simply put, SEO will help you rank higher for relevant keywords, bringing you more targeted visitors.
SEO works for physical products, services, blogs, and virtually any business where prospects search online.
For example, a landscaper might want to rank for a search query like “landscaping services near me.” Similarly, a vegan blogger might want to rank for the term “vegan oatmeal cookie recipe.” An ecommerce shoe store might want to rank for “high-heel shoes online.”
Once the searcher lands on your website, you can convert them into customers.
Is SEO easy to learn?
SEO basics are easy to learn, but becoming a master of SEO can take years as it requires experimentation and testing to figure out how to handle various edge cases.
We’ll teach you the basics of these three core concepts below, but the best way to learn is to create your own website and try it out yourself.
Does SEO still work in 2023?
SEO still works in 2023 as people are still searching for answers to their questions in search engines like Google.
You may have heard the phrase “SEO is dead.” It’s true that most of the older tactics people used a few years ago (such as keyword stuffing and spammy link building) no longer work, but that doesn’t mean that SEO is dead.
Effective SEO strategies are certainly different for 2023, especially with the introduction of AI. However, SEO will remain relevant as long as people search for answers to their questions.
What are the benefits of SEO?
Most marketing channels require you to pay to earn a visitor to your website. However, you don’t pay a cent when someone clicks on your website’s link in the organic search results.
Earning those top ranking positions in Google (and other search engines) requires you to create content, build relationships with others in the industry to earn backlinks, and maintain a website, which does cost money.
Nevertheless, once your content ranks, you can expect it to generate traffic at no additional cost.
This also means that while SEO takes some time to generate an ROI (Google won’t rank your content immediately), you’ll continue to earn great returns over the long run with little additional investment.
Finally, you have control over who you attract to your website based on the keywords you target and the content you write. As privacy issues continue to rise, ad platforms are becoming less reliable at accurately targeting customers, so SEO targeting is becoming comparatively more effective.
What are SEO basics?
The basics of SEO are:
- Technical foundation
- Content creation
- Link building
We’ll cover each one in detail below with step-by-step instructions so you can implement them yourself.
When you finish reading this post, you’ll have the 80/20 of SEO and can be a formidable competitor in your industry.
Technical Foundation
Similar to building a house, it’s important to have a solid technical foundation to build on. The term “technical SEO” scares many beginner SEOs, but the basics are quite simple.
You just need a website that is functional, secure, and easy to navigate. Most WordPress websites come like this out of the box, but you can also hire someone to create a functional website for you.
In fact, a key mistake many beginner SEOs make is focusing too much on the details of technical SEO rather than concentrating on higher-leverage opportunities like improving content quality.
Put simply, your website won’t be able to rank if it has major technical issues, though as long as it’s delivering a good user experience and Google can crawl and index all of the pages, you’ll likely see diminishing returns for minor technical optimizations.
Therefore, we’ll discuss the 80/20 of the technical SEO basics that are essential to get right as you build your website.
Step 1: Choose a Domain, CMS, And Website Hosting Platform
Every website requires a domain name (e.g., “amazon.com”), a CMS (content management system), and web hosting to exist online and be found by search engines.
As you choose your domain name, here are a few considerations:
WordPress.org, Wix, and Squarespace are all examples of CMS platforms, though WordPress.org is generally regarded as the most SEO-friendly.
As for web hosts, there are plenty of different options, though a few well-respected ones include Siteground and WP Engine.
You’ll also have to select a WordPress theme. This is the basic framework of what your website will look like, and the biggest consideration at this stage is to ensure you select a theme that looks good on desktop, tablet, and mobile devices.
We have a resource that provides a more detailed analysis on selecting the best WordPress tools, so feel free to check it out for more information. It also recommends the best places to purchase a domain name, WordPress themes, and even WordPress plugins.
It’s also important to add an SSL certificate to your website for security (and because it’s a Google ranking factor). This protects your website from hackers, and you can tell if a website has an SSL certificate as it will appear as HTTPS rather than HTTP.
Many web hosting packages include an SSL certificate, though you can also use a
Step 2: Lay Out The Site Structure
There are a few key elements that every website structure needs:
- Home Page: Your homepage should be just your domain name (e.g., “example.com”), and it should act as a conductor that helps people find the most relevant content. It’s generally best to avoid optimizing it for any particular keyword other than your brand’s name.
- About Page: This is important for EEAT reasons, as search engines want to know that you’re a legitimate website with authoritative information. Include bios of the founder, contributors, and any other information that helps earn the reader’s trust.
- Services/Product Pages: This is where you’ll include information about what you sell (if you sell anything).
- Resources/Blog: Content is a major aspect of SEO, so you’ll want a link to a blog or resource page in your main menu.
- Contact: Similar to the about page, a contact page is helpful for EEAT as it makes your website seem more legitimate. You can insert a contact form or simply write your contact information.
In the footer, include a Terms of Service and Privacy Policy page. Plenty of WordPress plugins can auto generate the text for these pages for you.
You might have additional pages in the main menu, like Pricing, Features, or Tools, but those mentioned above are critical for basic SEO. If you’re selling a service or SaaS product, you might also want to include a CTA like “Sign Up” or “Demo” in the menu as well.
Here’s an example of a well organized menu:
As you build out your blog and (if you’re an ecommerce website) product pages, you might be unable to fit them all in your main menu. So, as you create more content or add more products, create categories and interlink to child pages so that search engines and users can find what they’re looking for.
For example, instead of just inserting a link to “example.com/pink-lady,” create a category for fruits, and then a category under fruits for apples, and then place “pink lady” under those categories. So the URL might read “example.com/fruits/apples/pink-lady.”
Step 3: Execute On Page SEO Optimizations
Once your website is set up, here are the basic on-page optimizations to consider.
Title tag and meta description
The title tag and meta description appear in search results to tell both Google and users what your page is about.
The title tag should be no more than 60 characters, and the meta description should be no longer than 160 characters. It’s also important to include your target keyword in the title tag, meta description, and within the first 100 words of your page.
You can use the Yoast SEO plugin to fill out your title tag and meta description.
Site speed
Site speed is also a critical factor that impacts SEO, so use a tool like PageSpeed Insights to see how fast your site is, and then send the recommendations to a developer (even someone on Upwork) to fix it for you.
Optimize images
Google Image search is another massive opportunity to earn traffic, though few people optimize their images to rank.
The good news is that it’s fairly simple to optimize your images. Simply include the alt text by describing what the image is. For example, if the image is a picture of pink fuzzy slippers, label the alt text as “pink fuzzy slippers.”
Below, you can see that I named the screenshot of the editorial calendar “editorial calendar example.”
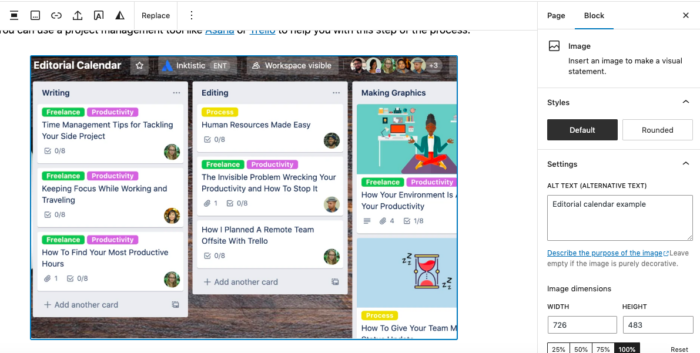
Reducing the image’s file size is also a good idea, as large media can slow your website down.
You can use a WordPress plugin like Jetpack to automatically reduce the file size.
User experience
Finally, user experience is becoming increasingly important – especially as search engines now compete with ChatGPT. So go through this checklist to make sure:
- The body font is large and clear (e.g., 12pt Sans Serif), making it legible even from several feet away.
- The navigation is clear, and the reader can easily find any page within 3-4 clicks.
- There aren’t too many pop-ups or distractions that annoy users.
Hotjar is an excellent example of a website with a great user experience:
Step 4: Set Up Google Search Console
Finally, it’s essential that you can tell which pages are indexed and if any errors might prevent pages from showing up in search engines.
Set up Google’s free tool, Google Search Console, to track this information.
It’s also important to track your website’s performance to see which pages drive the most traffic and conversions. To access more detailed analytics information, set up Google’s other free tool, Google Analytics.
It’s a rather complex tool, so consider taking Google’s analytics training if you don’t know how to use it.
Want us to
scale your traffic?
For the first time, The Copyblogger methodology is now available to a select few clients. We know it works. We’ve been doing it since 2006.
Content Creation
Once you’ve established a solid technical foundation, the next step is to create content so that your website shows up for search queries that your target audience types into Google.
If you don’t have any content that answers their search queries, there’s no reason for Google to rank your website.
Below, we’ll discuss how to conduct keyword research to uncover the search terms your ideal audience is searching for and then create well-optimized content to rank for those keywords.
Step 1: Keyword research
Keyword research is identifying the types of search terms your ideal audience types into Google before purchasing your products or services.
This step is important because it determines who visits your website. A great keyword research strategy will attract people actively looking to purchase your product or service.
We have a detailed guide to keyword research, though arguably the easiest method to quickly identify the best keywords is to simply look at your competitors’ keyword strategies.
To get started, select a competitor with a similar domain rating (sometimes referred to as “domain authority”) to your website’s domain rating. (You can view a website’s domain rating by plugging it into Ahrefs or SEMrush.) If you’re starting a brand new website, find any competitor with a domain rating of under 15.
Next, sort by “top pages” to identify the keywords that bring them the most traffic. I like to further sort the results by “value” as traffic and value are not always correlated.
Pro Tip: If I’m looking for keywords to target specifically for content creation, I usually sort by blog pages only. For example, instead of typing “example.com” into the search bar, I’ll type in “example.com/blog” and then set it to “path.” This way, I only get blog posts rather than product or service page keywords.
Then, you can click on the page to see all the variations of the keywords it ranks for. Select the keyword variation with the highest volume and lowest difficulty and add it to a spreadsheet of keywords to target.
Given that the competitor domain you’re using has similar authority to your website’s authority, you can probably rank for these same keywords.
Repeat this process for several more competitors, and eventually, you’ll have a list of valuable keywords to add to your spreadsheet.
Step 2: Create a Content Strategy
Now that you have a list of keywords, it’s time to create a content strategy to rank for those keywords. First, prioritize the keywords by purchase intent and value to your brand.
For example, if you sell dog toys, the keyword “best puppy toys” is a much more valuable keyword than “how to house train a puppy” because the first one suggests the searcher is actively looking for the product you sell and has purchase intent.
In contrast, if you offer dog training services, the second keyword is more valuable as the pain point the searcher typed in is something you solve.
Once you’ve prioritized the keywords, create a content calendar that outlines how often you plan to publish and who is in charge of each step.
You can use a project management tool like Asana or Trello to help you with this step of the process.
The key to winning with content marketing is consistency, so select a publishing cadence that your team can realistically achieve. Otherwise, you might start and then burn out.
Step 3: Create The Content
Before creating the content, do a quick Google search for the keyword as that top ranking result is your cheat sheet for what kind of content Google wants to rank.
As you analyze the content, answer these questions:
- What is the format of the content? (e.g., is it a list post or a guide?)
- How long is the article? (1,000 words, 2,000 words?)
- What subtopics do they discuss in the article?
- What unique aspects do they include in the content? (e.g., case studies, examples, etc.)
Repeat this analysis for all of the blog posts on the first page of Google.
Google and other search engines strive to rank the most useful content to the reader, so the key to writing an SEO-friendly blog post is using the analysis above to create a more thorough and unique blog post than any of the other pieces of content on Google.
You should also include the main target keyword in the title, and you can also use a tool like Clearscope to ensure you include other relevant, related keywords in the body of the blog post.
You won’t see immediate results from your content marketing efforts, though over time, your rankings will rise and you’ll see an ROI.
Link Building
Google has directly stated that backlinks and content are the two most important ranking factors they look at, and this still holds true in 2023.
So, what is a backlink?
A backlink is a hyperlink on one website that enables the reader to navigate to another website.
The above text, “Google has directly stated,” is an example of a backlink.
However, the website that the reader lands on is the one that benefits from the link.
In the example above, Search Engine Land is the one that benefits from the backlink as we’re sending our traffic to that website.
Google uses backlinks to help understand whether or not a website is credible. Unfortunately, search engines can’t directly analyze information accuracy and quality, so they instead use backlinks to determine if a source is trustworthy and publishes quality information.
It makes sense.
If many websites in an industry reference a specific website, the one referenced is probably fairly credible. In the example graphic below, all those health websites link to Harvard’s website.
Search engines figure that if all those credible healthcare websites link to Harvard, Harvard must be an authoritative and trustworthy source in the healthcare industry.
However, there’s a caveat.
Not all links are equally valuable.
As you can see in the example above, all of the other websites linking to Harvard also have many links to them and are in the healthcare space. If Harvard had a gaming website linking to it, that wouldn’t make Google believe that Harvard is an authority in healthcare.
Therefore, you want backlinks from websites that are:
- Relevant to your industry
- From high-quality websites
For example, let’s say you’re a travel blogger. In that case, here are a few different scenarios where:
- Low quality: Backlink from Apple.com = High quality website but irrelevant to your industry.
- Low quality: Backlink from unknown travel blog (DA 10) = Low quality website but industry relevant.
- High quality: Backlink from Nomadic Matt (DA 70+) = High quality website and industry relevant.
Unfortunately, earning links is difficult. However, here are two options to earn links:
- Build them manually.
- Earn them organically.
If your website is relatively unknown, you will probably have to do some manual link building.
This involves directly contacting another website and offering value in exchange for a link.
The most common forms of “value” to receive a link include:
- Broken link building: If the other website has a broken link and you have a similar resource, you can ask them to replace the link.
- Unlinked mention outreach: If a website mentions you or uses an image from you, ask them to add a link to the source.
- Guest posting: Writing on an industry-relevant publication.
- Paid sponsorship: You can simply pay a blog to link to your website.
The problem with these methods is that response rates tend to be under 5%.
In fact, the only one that I would probably still recommend is strategic guest posting. If you guest post on a website that has your ideal audience.
For example, if I was growing a website in the SEO space, I’d probably try to become a regular guest post contributor on industry publications like Search Engine Journal, The Content Marketing Institute, and even some private blogs that have a large SEO readership, like Ahrefs.
By guest posting on these websites, you’re earning links and getting in front of your ideal audience. As you can see, this guest post generated nearly 5,000 reads and plenty of shares, so you also get the benefit of building your brand’s presence.
Nevertheless, guest posting doesn’t scale very well, so I recommend that you attract links.
In other words, you publish content that people want to link to.
What kinds of content attract links?
Typically, original research, statistics pages, case studies, and other data-driven posts drive links, as content marketers need data to support their claims.
Brian Dean also introduced a tactic he calls Reverse Outreach, where he creates blog posts for keywords that journalists are clearly searching for, like “how many people own bitcoin?”
To find these journalistic keywords, do a quick Google search for “(your industry) statistics.”
Then, identify the statistic that earns the most links for the top ranking page.
For example, this statistic pops up frequently:
Then, create a single blog post where the title tag is the question that the statistic answers.
For example, I’d create a blog post titled “How much is the horse industry worth?”
I might also create one for “How many people own horses?”
This is how Brian Dean helped Exploding Topics earn thousands of backlinks in just two years:
Get started With SEO Basics
There you have it — the basics of SEO. If you follow each step in this guide, you’ll be well on your way to SEO success. While it isn’t difficult to implement an SEO strategy, consistency is the key to success.
Most websites require many months of consistent SEO practice before they see strong results, but the good news is that these results compound over time.
So create a schedule to implement each of these tactics and get started on it today.
Or if you’d prefer, you can hire us to handle your SEO for you.